Select an Authentication Method for Website
The Website content source can be authenticated using five methods. This article provides an overview of all five methods.
-
No Authentication
-
Basic Authentication
-
Form
-
Multi-Step Form
-
NTLM
-
Basic Authentication via Htaccess
Once you have authenticated the content source, return to Use a Website as a Content Source.
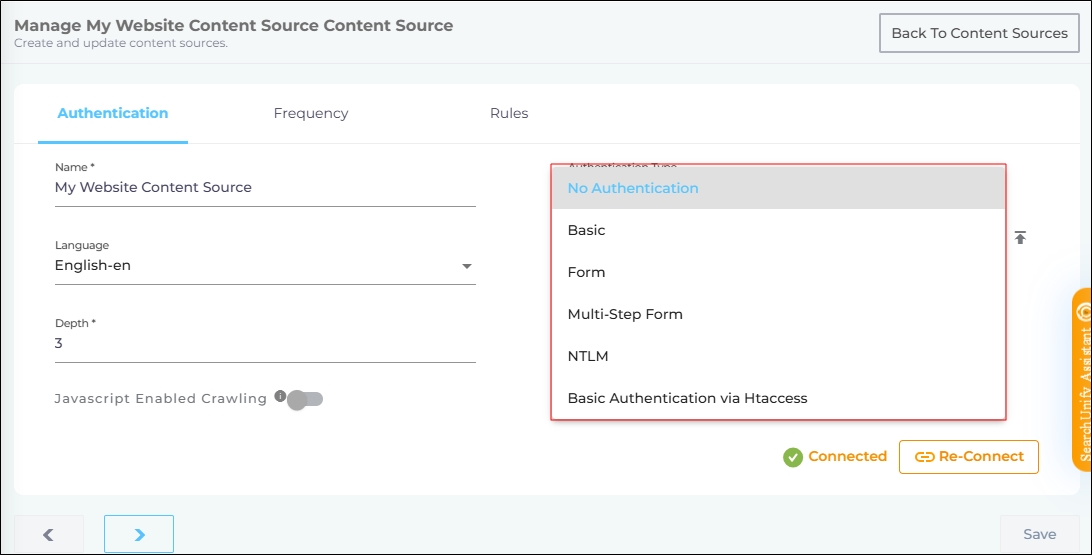
Fig. A snapshot of all the authentication options for the Website content source.
No Authentication
This authentication method is adequate if your website is public. SearchUnify Docs are an example of a public website. They are accessible to everyone with an internet connection. To crawl a public website, select No Authentication as the authentication method and click Connect.
However, if your website requires users to log in before they can view an article, a video, or other content, you must select another authentication method.
Basic Authentication
Note.
A website cannot be crawled using the Basic Authentication method if it is protected by a CAPTCHA
Select Basic from the Authentication Method drop-down if the website requires users to enter their username and password before they can view content. When you select Basic as the authentication method, two new fields appear. After entering a valid username or email, and password in those fields, click Connect.
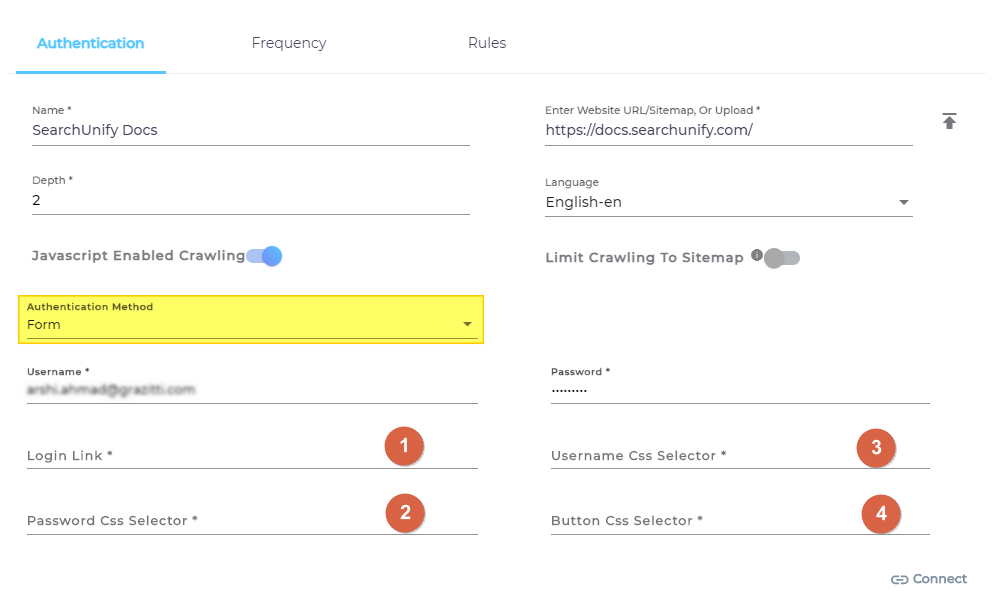
Form
Note.
A website can be crawled using the Form Authentication method only if JavaScript-enabled crawling is turned on.
Form is an advanced version of the Basic authentication method. Authentication with Form is attained using CSS selectors. This authentication type is used when a website is gated and requires users to fill out a login form to access the website.
You can think of CSS selectors as markers that guide a browser in interpreting data.
Consider the following image, where <h2> tags tell the browser to interpret the text contained within them as a second-level heading, and <p> tags tell the browser to interpret the text contained within them as a paragraph. Both are examples of CSS selectors.
Fig. A snapshot of two selectors: h2 and p.
When you select Form-based authentication, specify, in addition to the username and password:
-
Login URL: The Login URL is the URL where the login screen is displayed.
-
CSS selector for the username field
-
CSS selector for the password field
-
CSS selector for the login button
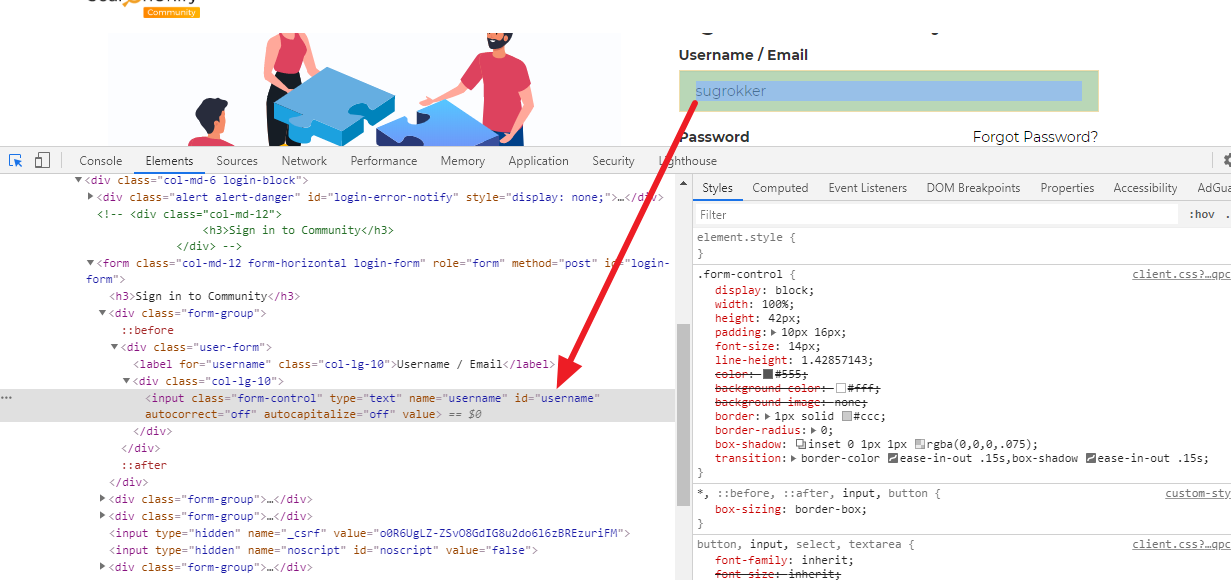
Chrome users can find the CSS selectors by pressing Ctrl+Shift+I and hovering the cursor over each field and button one at a time.
In the next image, you can see the CSS selector for the username field, which is #username.
Fig. A snapshot of the username field and its CSS selector #username.
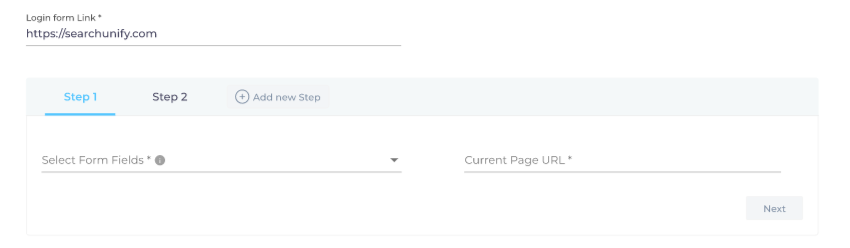
Multi-Step Form
A Multi-Step Form allows you to crawl websites where two or more successful logins are required. You can enter the credentials required to log in at each stage of the Multi-Step Form.
Fig. A snapshot of Multi-Step Authentication method on a website content source.
Enter a Login Form URL where you want to deploy the multi-step form authentication. In Select Form Fields, choose the authentication fields you want to deploy in this step. For example, you can deploy the username and password mechanism in step 1, and the client ID and client secret-based mechanism in step 2, and so on.
After entering all the required details, click Connect.
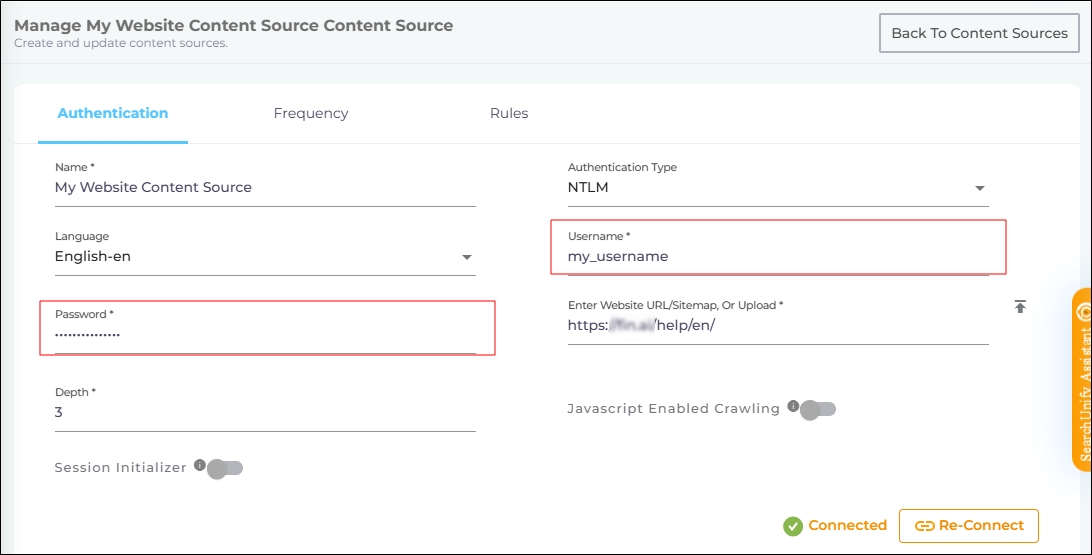
NTLM
On the frontend NLTM is similar to Basic Authentication where you enter your username and password. However, in the backend, it’s a much more secure protocol because along with the username-password combination, the domain is also authenticated. If you are on a Windows server, select NTLM protocol and enter your Username and Password.
Fig. A snapshot of NTLM method on a website content source.
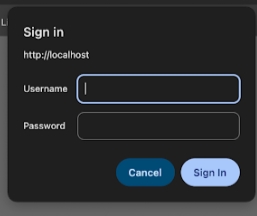
Htaccess via Basic Authentication
Htaccess allows changes to be made in the directories. You can use Htaccess to configure access to the data stored on your website. This method is safe because the person using Htaccess has access only to the directory where the .htaccess files reside, along with its subdirectories. If you see the following login dialog on your content source, select Basic Authentication via Htaccess to crawl it.
Fig. A snapshot of a content source where Htaccess is required.
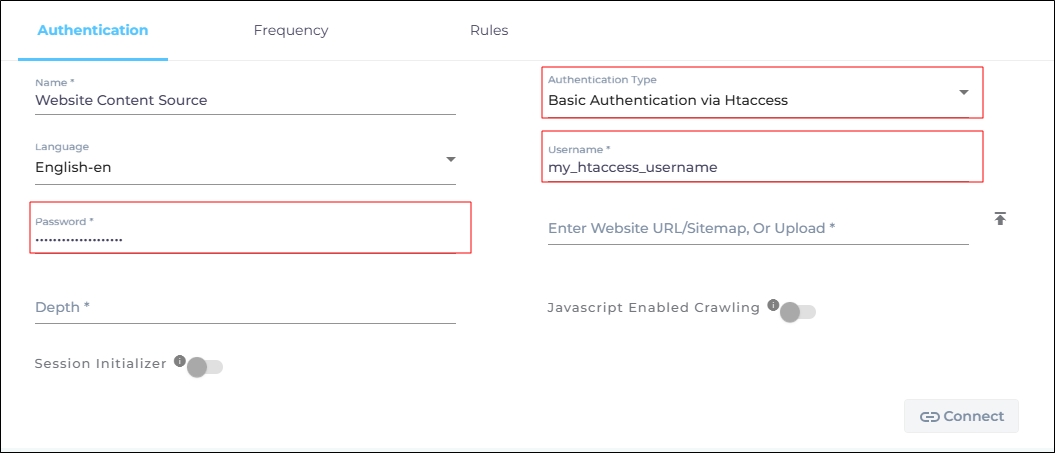
To use Htaccess to authenticate your content source, first select Basic Authentication via Htaccess, then enter the following details:
-
Htaccess Username: Enter your .htaccess username.
-
Htaccess Password: Enter your .htaccess password.
Fig. A snapshot of Htaccess via Basic Authentication method on a website content source.