Use SharePoint As a Content Source
This article walks you through the process of installing SharePoint as a content source.
PREREQUISITES
You can only crawl the data related to documents, pages, and lists.
You have to be an admin to crawl SharePoint site data. If you are not an admin, then you can crawl only the sites accessible to you.
Any SharePoint user can crawl community sites.
Data returned from SharePoint may be throttled. Take a look at the latest SharePoint rate limits.
Attachment types crawled in SearchUnify are PDF, DOCX, TXT, DOC, PPT, PPTX, CSV, XLS, and POTX.
Establish a Connection
-
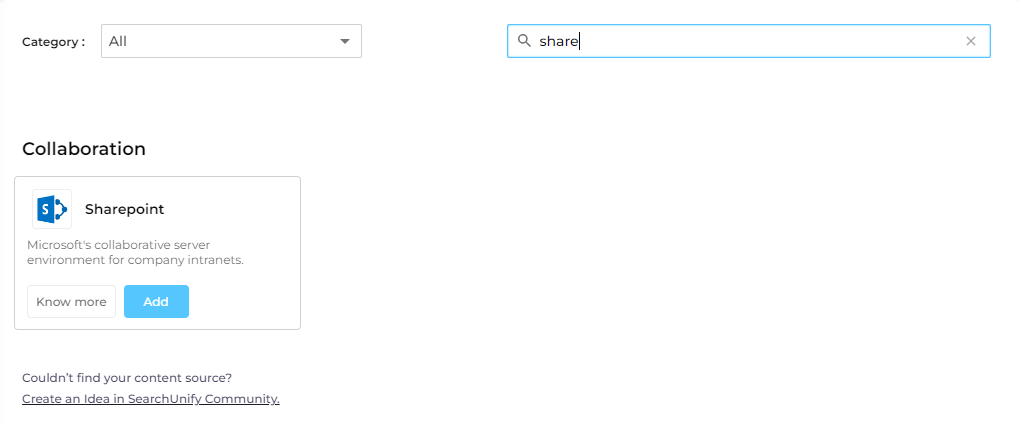
Find SharePoint from the search box and click Add.
-
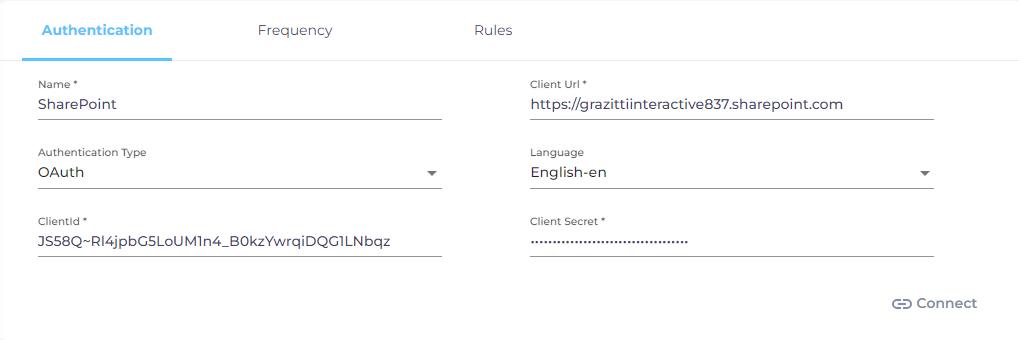
Under the Authentication tab, enter the required details:
-
Name. Enter a label. Labels help you distinguish content sources from one another.
-
Client URL. Enter the SharePoint instance web address.
-
Authentication Type. Select either Basic or OAuth.
-
Selecting Basic requires you to enter your SharePoint login ID and password.
-
Selecting OAuth required you to enter Client ID and Client Secret. This article explains how to Obtain Client ID and Client Secret for SharePoint Authentication .
-
- Language. Select the content language.
-
- Click Connect.
Once the connection has been set up successfully, you will be prompted to the next action - Set Frequency.
Re-Connect
The Authentication screen is displayed when an already-created Content Source is opened for editing. An admin can edit a Content Source for multiple reasons, including:
-
To reauthenticate
-
To fix a crawl error
-
To change frequency
-
To add or remove an object or a field for crawling
When a Content Source is edited, either a Connect or a Re-Connect button is displayed.
-
Case 1: When the Connect button is displayed:
-
When the Connect button is displayed if the Content Source authentication is successful. Along with the button, a message is displayed There are no crawl errors and the Content Source authentication is valid.
-
Fig. The Connect button is displayed on the Authentication tab.
-
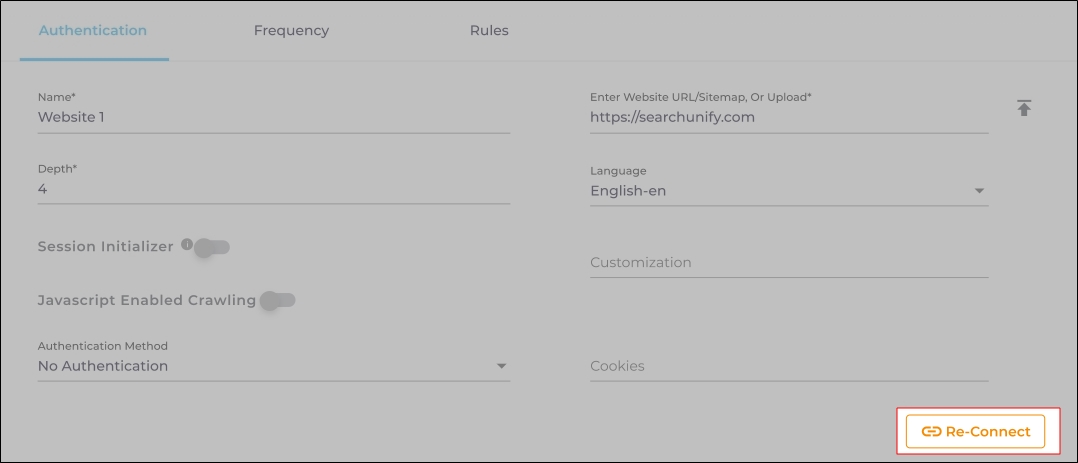
Case 2: When the Re-connect button is displayed:
-
The Re-connect button is displayed when the authentication details change or the authentication fails for any reason.
-
In both cases, the Content Source connection must be authenticated again. To reauthenticate a Content Source, enter the authentication details, and click Re-Connect.
-
Fig. The Re-Connect button is displayed on the Authentication tab.
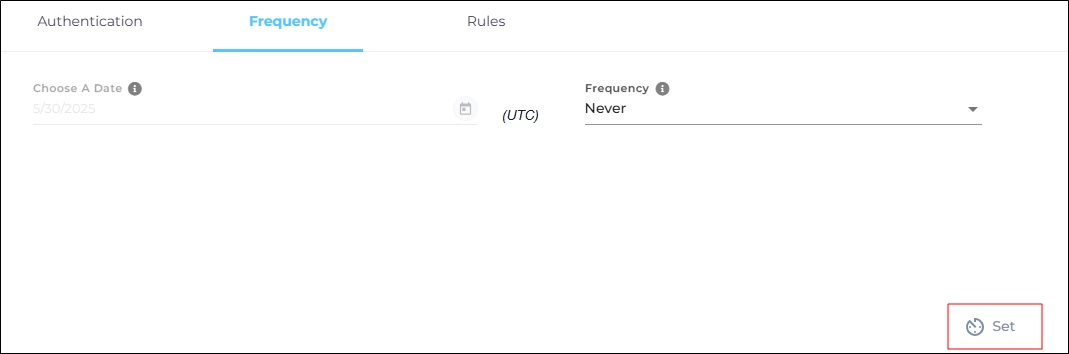
Set Up Crawl Frequency
For this content source, the Choose a Date feature is grayed out. That's because during each crawl all the data is indexed from scratch. You can select the crawl frequency after configuring the content source. For now, click Set.
Fig. The Frequency tab when "Frequency" is set to "Never".
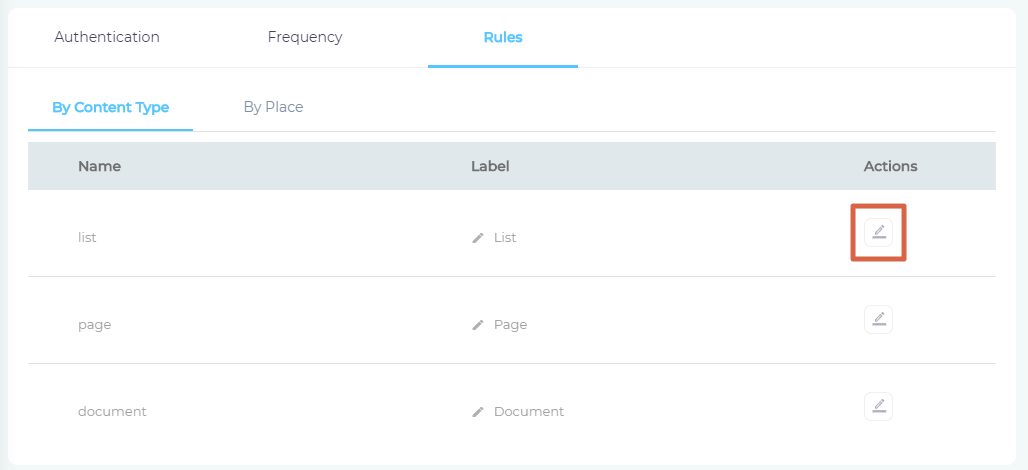
Select Fields and Websites for Indexing
SearchUnify can index three SharePoint content types: list, page, and document. Under the Rules tab, you will land on By Content Type subtab. You can further define which properties (content fields) of these content types are to be indexed.
-
Click
 to view the pre-configured properties of a content type.
to view the pre-configured properties of a content type.NOTE. You can add or delete the content fields. Although, it is not recommended for users other than Admins to make any changes in the fields.
- Navigate to By Sites subtab and use the alphabetical index to find and select your SharePoint websites that you want to index.
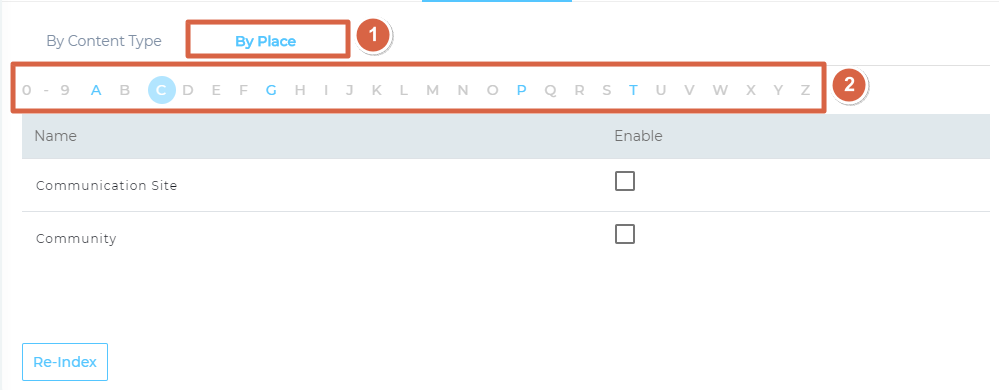
- Save your settings.
You have successfully added SharePoint as a content source in SearchUnify. Perform a manual crawl to start indexing data in SearchUnify.
Related
Find and Replace
Users on the Q2 '24 release or a later version will notice a new button next to each object on the Rules screen. It resembles a magnifying glass and is labeled "Find and Replace." You can use this feature to find and replace values in a single field or across all fields. The changes will occur in the search index and not in your content source.
Fig. The "Find and Replace" button on the Rules tab in the Actions column.
Find and Replace proves valuable in various scenarios. A common use case is when a product name is altered. Suppose your product name has changed from "SearchUnify" to "SUnify," and you wish for the search result titles to immediately reflect this change.
-
To make the change, click
 .
. -
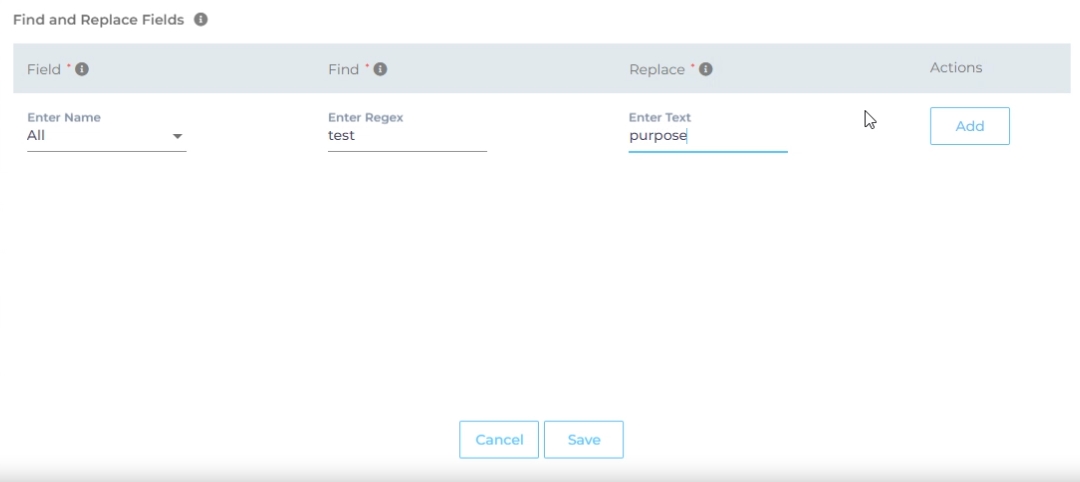
Now, choose either "All" or a specific content source field from the "Enter Name" dropdown. When "All" is selected, any value in the "Find" column is replaced with the corresponding value in the "Replace" column across all content source fields. If a particular field is chosen, the old value is replaced with the new value solely within the selected field.
-
Enter the value to be replaced in the Find column and the new value in the Replace column. Both columns accept regular expressions.
Fig. Snapshot of Find and Replace.
-
Click Add. You will see a warning if you are replacing a value in all fields.
-
Click Save to apply settings
-
Run a crawl for the updated values to reflect in the search results.
After the First Crawl
Return to the Content Sources screen and click ![]() in Actions. The number of indexed documents is updated after the crawl is complete. You can view crawl progress by clicking
in Actions. The number of indexed documents is updated after the crawl is complete. You can view crawl progress by clicking ![]() (View Crawl Logs) in Actions.
(View Crawl Logs) in Actions.
Once the first crawl is complete, click ![]() in Actions to open the content source for editing, and set a crawl frequency.
in Actions to open the content source for editing, and set a crawl frequency.
-
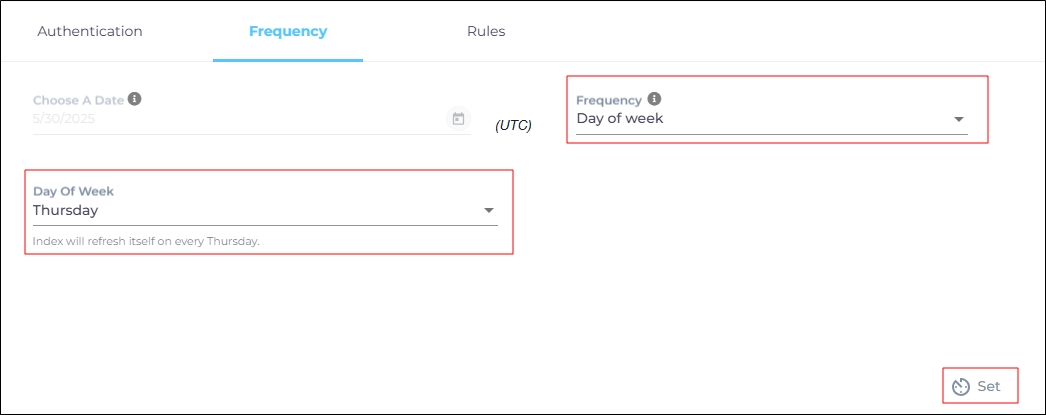
For this content source, the Choose a Date feature is grayed out. That's because during each crawl all the data is indexed from scratch. You can select the crawl frequency after configuring the content source. The following options are available for the Frequency field:
-
When Never is selected, the content source is not crawled until an admin opts for a manual crawl on the Content Sources screen.
-
When Minutes is selected, a new dropdown appears where the admin can choose between three values: 15, 20, and 30. Picking 20 means that the content source crawling starts every 20 minutes.
-
When Hours is selected, a new dropdown is displayed where the admin can choose between eight values between 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24. Selecting 8 initiates content crawling every 8 hours.
-
When Daily is selected, a new dropdown is displayed where the admin can pick a value between 0 and 23. If 15 is selected, the content source crawling starts at 3:00 p.m. (1500 hours) each day.
-
When Day of Week is selected, a new dropdown is displayed where the admin can pick a day of the week. If Tuesday is chosen, then content source crawling starts at 0000 hours on every Tuesday.
-
When Day of Month is selected, a new dropdown appears where the admin can select a value between 1 and 30. If 20 is chosen, then content source crawling starts on the 20th of each month.
It is recommended to pick a date between the 1st and 28th of the month. If 30 is chosen, then the crawler may throw an error in February. The error will be “Chosen date will not work for this month.”
-
When Yearly is selected, the content source crawling starts at midnight on 1 January each year.
-
-
Click Set to save the crawl frequency settings.
-
Click Save.