Search Report
Search Report lists end-user queries on search clients. The queries are divided into four sub-reports:
-
All Searches. It displays a list of all the 50 latest queries looked up on a search client. To dig deeper, use pagination.
-
Successful Searches (Clicks). It is a list of queries which returned at least one result and at least one of the results is clicked.
-
Searches with no Click. It is a list of queries for which results are found but not clicked. This data assists content managers identify documents whose titles and summaries can be rewritten to improve perceived relevancy.
-
Searches with no Result. Search queries for which no result is produced. A search can be no-result for multiple reasons:
-
Documents with the search keywords do not exist in your data repositories
-
The user does not have the permission to see documents.
-
Your search client is not connected with the content source where the documents are stored.
-
Sub-report Metrics
Each sub-report has four metrics. Searches with No Result is the sole exception with five metrics. Next, the table outlines the metrics.
The table on the right has a searchable and three sortable columns:
| № | Column | Displays | Extra Functions |
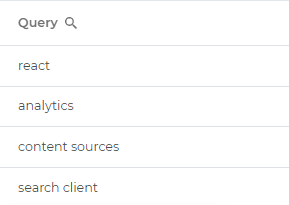
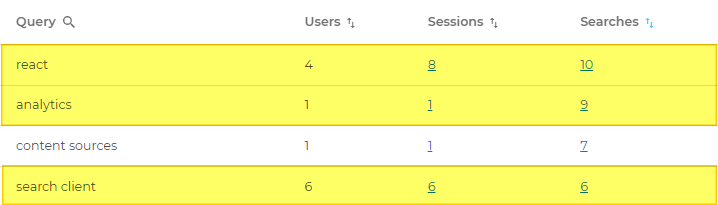
| 1 | Query | Search queries. Example. At least one user searched react, analytics, content sources, and search client. |
You can find a query in this column through the built-in search function. |
| 2 | Users |
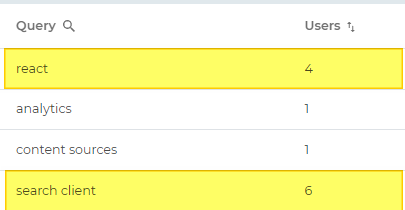
Number of unique devices (browsers) from which search queries occur.
Example: Four unique users searched react and 6 unique users searched search client. |
The column is sortable. |
| 3 |
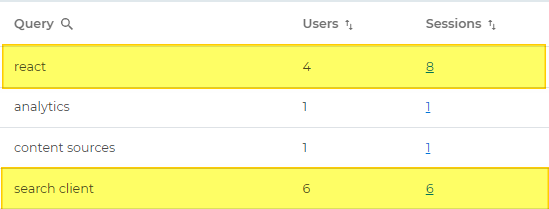
Sessions | Number of search sessions in which the queries occur. Example. Four unique users searched react in 8 different sessions and 6 unique users searched search client in 6 different sessions. |
The column is sortable. |
|
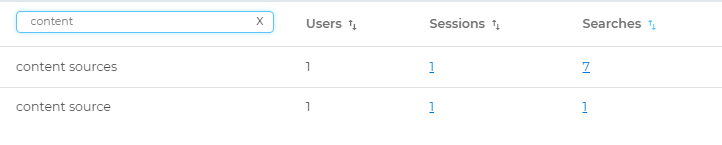
You can find the ID of each session.
Example. content sources has been searched in 4 different sessions. To find the ID of each session, click 4. The dialog changes and you see a four-table column with the session IDs, the email of the user who searched the query (only for Internal users), and the time of search. The Session ID and Email columns are searchable. The Last Search column is sortable.
|
|||
| 4 | Searches |
Number of times search queries repeat.
Example. Four unique users searched react 10 times in 8 different sessions, six unique users searched search client 6 times in 6 different sessions, and only one user searched analytics 9 times in one session. |
This column is sortable. |
|
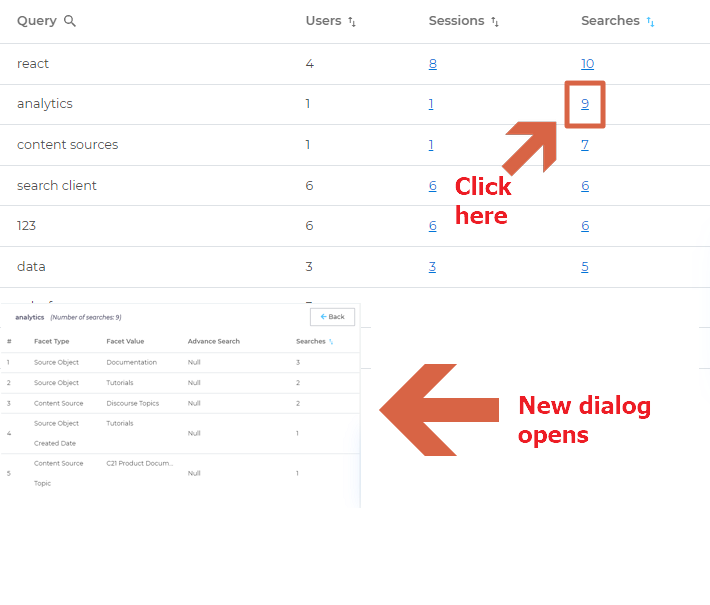
You can find out if what facets and advanced search operators are used with a query by clicking Searches.
Example. analytics has been searched 9 times. Click 9 in Searches. A dialog opens where you can see the facets or advanced search operators applied.
|
|||
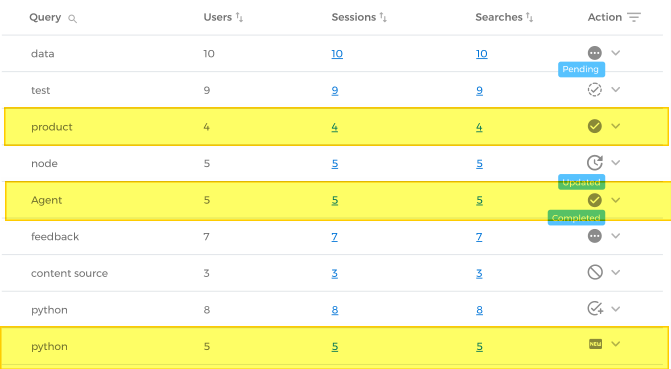
| 5 | Action (only for Searches with No Result) |
What has been done to address zero results queries.
Example. New content is required for python and someone has already made the changes to prevent Agent and product from being zero-result searches again. The column is visible only when a search client has been specified in Select Search Client. |
The column has eight filters, All and the following seven:
|
|
From Example. To find queries that new content, select New Content. NOTE. Filters are reset each time an SU Admin logs out, change the search client, or picks a new date range. Navigating inside the instance or refreshing the page through F5 has no impact on filter selection. |
Group Searches
With this Group Searches feature, search queries are organized into groups based on similarity, creating clusters that make it easier for users to analyze and explore specific patterns and make better strategic decisions to improve user experience.
When Group Searches is toggled on then similar queries are displayed in groups and it improves the efficiency and effectiveness of search query analysis.
Note. It is turned-off by default.
The Search Report displays the following information:
-
Query Group: A name for the query group. This name changes each time the clustering analysis is performed in the backend, which happens every other day. The field is searchable.
-
Eye Icon: Click it to view the queries in the Query Group.
-
Queries: It shows the number of distinct queries that occurred in the Query Group cluster.
-
Users: It shows the number of unique users that performed searches with the Query Group cluster.
-
Sessions: It shows the number of sessions where searches within the Query Group cluster occurred. The number of sessions can be greater than the number of queries because a query can repeat in several sessions. Click the number of sessions to view all the sessions IDs.
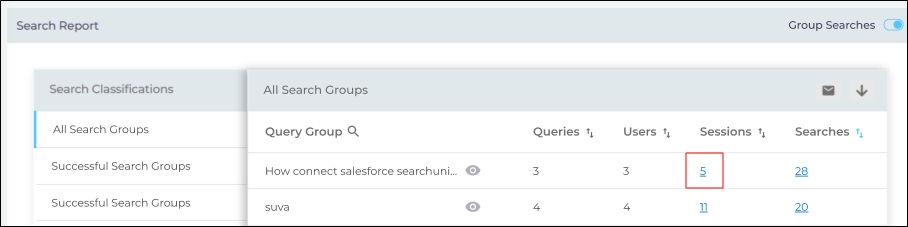
Fig. A snapshot of the clickable Sessions count.
You can further view the session history by clicking a session ID.
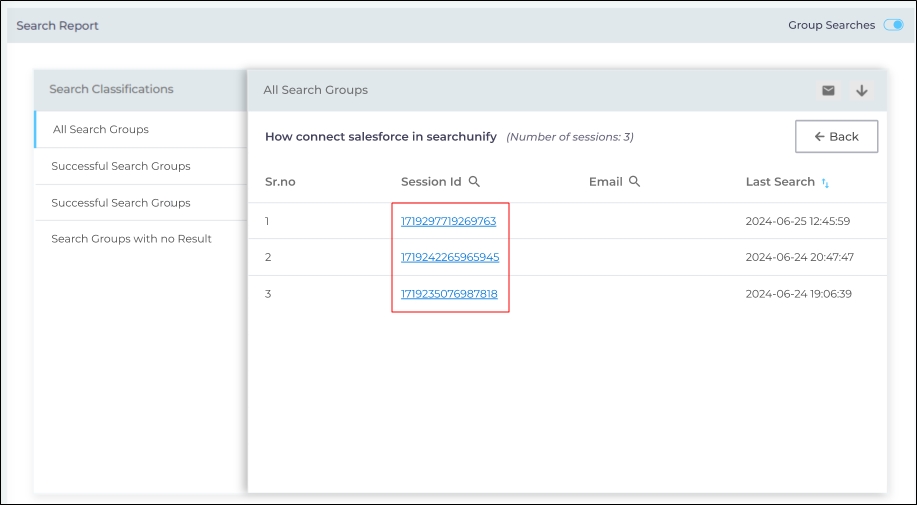
Fig. A snapshot of the clickable Session IDs.
-
Searches: It is the total number of searches within the Search Query cluster. You can find out what facets and advanced search operators are used with a query by clicking Searches.
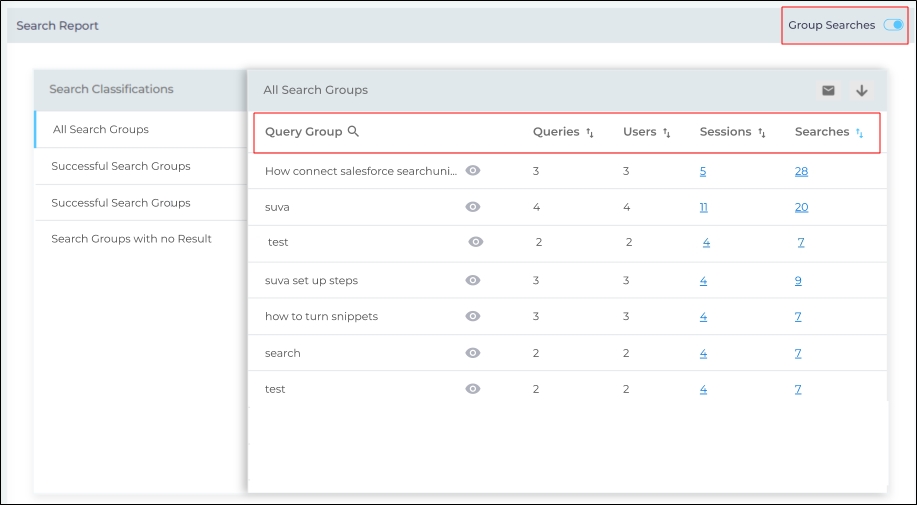
Fig. A snapshot of the Search Report when the Group Searches toggle is own.
When the Group Searches toggle is on and the search report is downloaded, then the group of each search query is displayed in column B, as shown below.
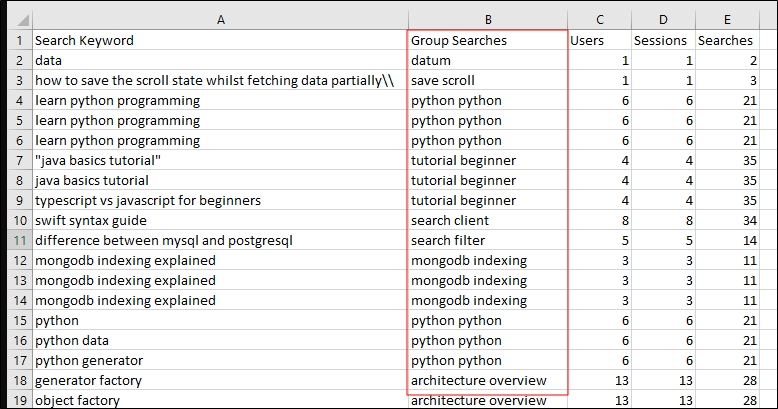
Fig. A downloaded Search Report with “Group Searches” toggle on.
Download or Share
Check out Download and Share an Analytics Report
NOTE.
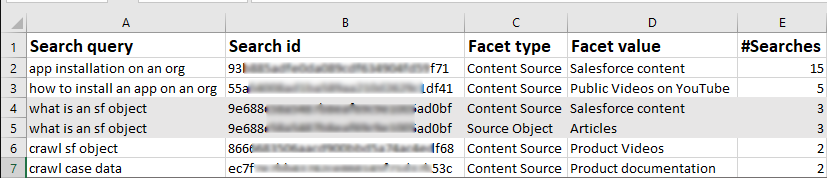
The downloaded or share reports for each classification are CSV files. Each CSV file consists of five columns: Search Query, Search ID, Facet Type, Facet Value, and #Searches, of which only Search ID is new. (#Search is the synonym of Count here.)
A user can apply multiple facets in a search query. Because each Facet Type and Facet Value occupies its own row, the Search ID helps readers immediately see which queries spread over multiple rows are essentially one. In the next image, row 4 and 5 refer to the same query because their Search ID is identical.
A report can contain data for up to 5,000 search queries.
Related Documents