Relevancy Configurations: Default Search Operator, Special Character Search, Relevance Score, Neural Search, Hybrid Search
The Relevancy tab includes the following settings:
-
Search Operator – Defines the default relationship between two or more keywords.
-
Special Characters Search – Controls how non-alphanumeric characters are processed during a search.
-
Relevance Score – Displays the relevance score for each search result.
-
Neural Search – Continuously learns from user interactions and improves relevancy over time by adapting to evolving search behaviors and content patterns.
-
Hybrid Search – Combines Neural and Keyword search to enhance relevancy by balancing semantic understanding with exact keyword matching for comprehensive search results.
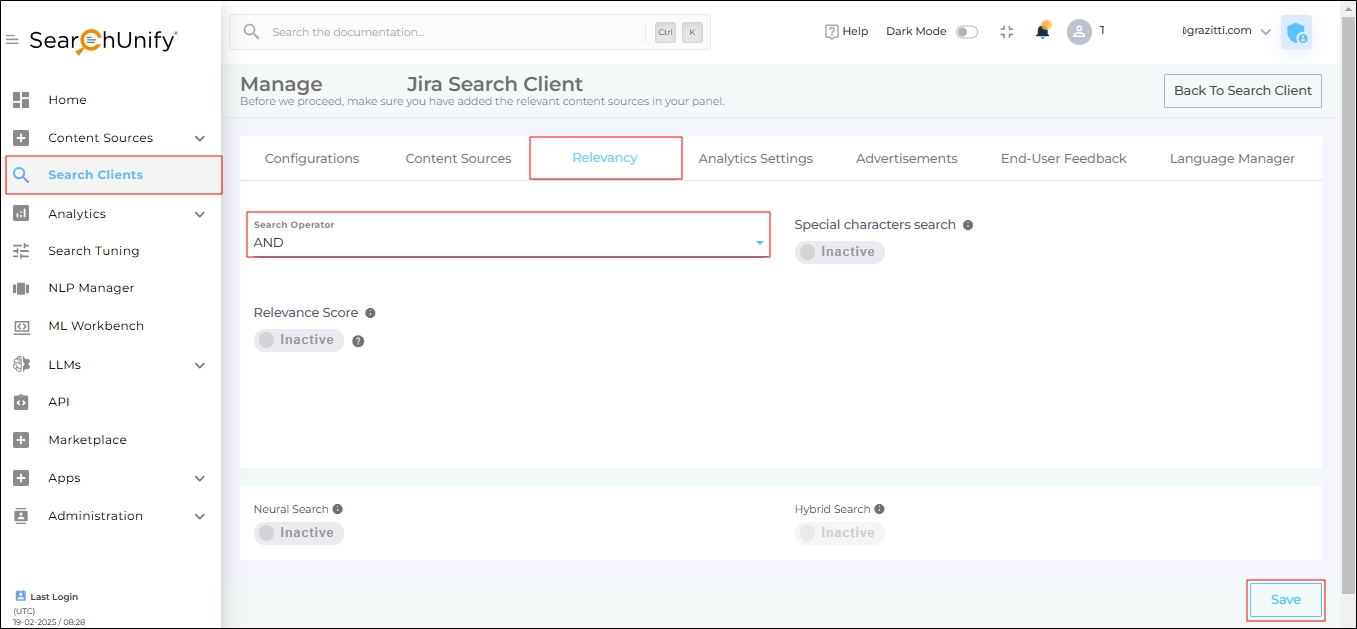
Search Operator
This setting has two options:
-
AND. A query like "search clients" is interpreted as "search” AND “clients." The results include only documents that contain both the words.
-
OR. A query like "search clients" is interpreted as "search” OR “clients." The results include documents that contain either "search" or "clients" or both.
To select a search operator, follow these steps:
-
In Search Clients, open a search client for editing.
-
Click the Relevancy tab.
-
In the Search Operator dropdown, select OR or AND.
-
Save your settings.
Fig. The Search Operator dropdown in the Relevancy tab.
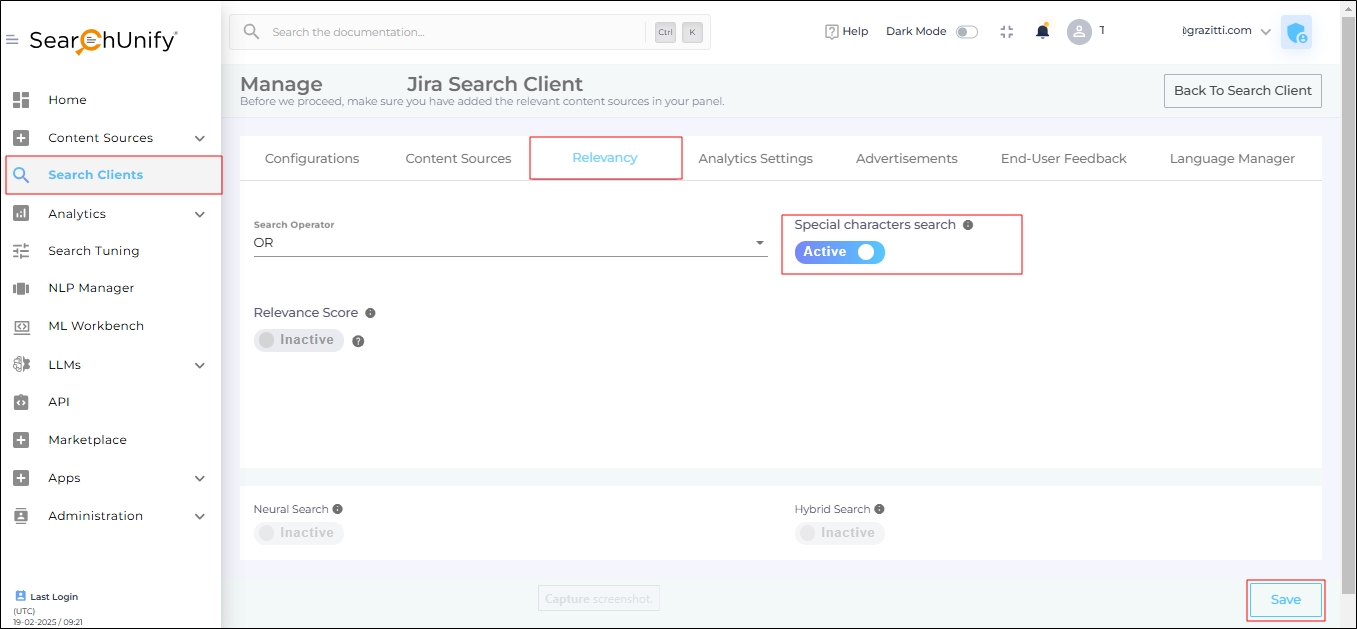
Special Characters Search
In queries like [#search +client], where the “#” symbol is used at the beginning, the “+” sign functions as an advanced search operator. However, this creates an issue when users search for terms like [C++], where “+” is a part of a query and not an operator.
To allow users to search for special characters, enable Special Characters Search by following the steps given below:
-
In the Search Clients, click the Edit icon to open a search client for editing.
-
Click the Relevancy tab.
-
Toggle on Special Characters Search.
-
Save your settings.
Fig. The Special Character Search toggle in the Relevancy tab.
When Special characters search is on, you can search using the following characters.
| № | Searchable Character |
| 1 | Ampersand (&) |
| 2 | At Sign (@) |
| 3 | Greater Than (>) |
| 4 | Less Than (<) |
| 5 | Dollar ($) |
| 6 | Percentage (%) |
| 7 | Caret (^) |
| 8 | Equals (=) |
| 9 | Colon (:) |
| 10 | Full stop(.) |
| 11 | Forward slash (/) |
| 12 | Hyphen (-) |
| 13 | Plus (+) |
| 14 | Asterisk (*) |
Special characters can be searched as long as the query does not start with #.
5 > 2: Works
# 5 > 2: Doesn't work
# 5 > 2 OR 3: Doesn't work
Exception:
Special characters can be searched in an advanced search if they are enclosed in quotes.
-
# "5 > 2"works.
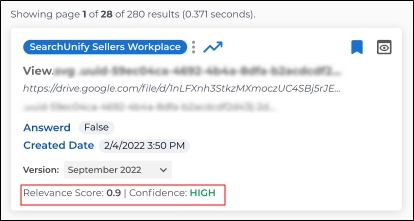
Relevance Score
Enabling Relevance Score displays two numbers alongside each search result:
-
Relevance Score
-
Confidence Level
Fig. A snapshot of a result with Relevance Score and Confidence Level.
The Relevance Score measures how relevant a search result is to a user's query. It is based on two factors:
-
Result relevancy – Calculated in real time at the backend using SearchUnify’s search algorithms.
-
User Clicks – Serves as a proxy for relevance, considering the total number of clicks a result receives.
The Relevance Score is obtained by normalizing result relevancy and user clicks into a value between 0 and 1, where:
-
0 indicates an irrelevant result
-
1 indicates a highly relevant result
The score is always a multiple of 0.1 (e.g., 0.2, 0.3, 0.4), but never 0.35 or 0.49. It is dynamic and updates at regular intervals.
The Confidence Level represents the accuracy of the Relevance Score as perceived by SearchUnify’s algorithms.
All search results are ranked in descending order based on their Relevance Score and then divided into three equal groups:
-
High Confidence – Top one-third of results
-
Mid Confidence – Middle one-third of results
-
Low Confidence – Bottom one-third of results
Example: Consider nine documents with the following Relevance Scores: 0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.3, 0.5, 0.4, 0.11, 0.9.
-
Arrange them in the decreasing order: 0.9, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.1.
-
Split them into three parts: [ (0.9, 0.6, 0.5) || (0.4, 0.4, 0.3) || (0.2, 0.2, 0.1) ]
-
Label the parts:
-
High Confidence: (0.9, 0.6, 0.5)
-
Mid Confidence: (0.4, 0.4, 0.3)
-
Low Confidence: (0.2, 0.2, 0.1)
-
NOTE.
A high confidence but low score result is a symptom of a content gap or a lack of relevancy tuning.
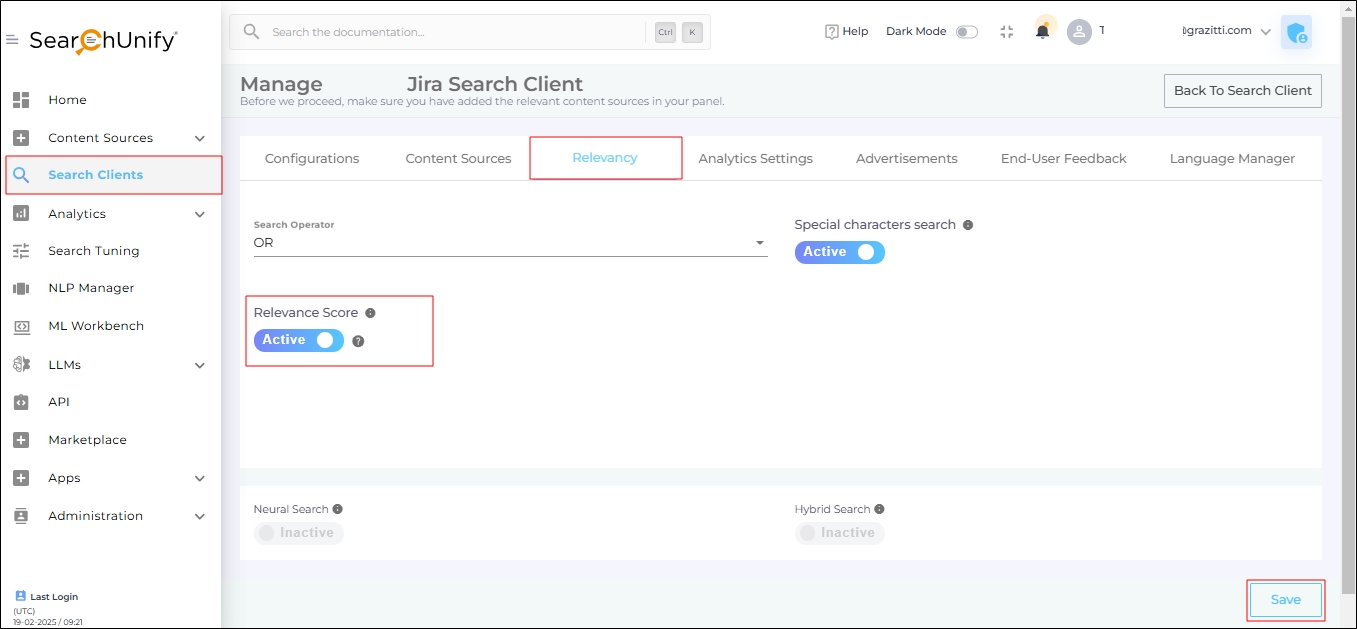
To turn on Relevancy Score:
-
In Search Clients, open a search client for editing.
-
Click the Relevancy tab.
-
Toggle on Relevancy Score.
-
Save your settings.
Fig. The Search Relevancy Score toggle in the Relevancy tab.
NOTE.
Neural and Hybrid Search work in either Real-Time mode or Frequency-Mode. More information about these modes is on Neural-Hybrid-Search.htm.
Neural Search
Neural Search leverages machine learning (ML) algorithms and natural language processing (NLP) to understand the intent and meaning behind search queries.
For more details, visit Neural and Hybrid Search.
Hybrid Search
Using search client specific granular vectorization, embedded type support, partial vectorization at the level of search client, and up to nine embedding models are now supported, Hybrid Search combines the strength of keyword search and vector search. Both vector search and keyword search are used simultaneously to provide contextually relevant search results. The SearchUnify team can, on the request of a customer, tweak the share weight of keyword and vector search.
To learn more, visit Neural and Hybrid Search.